- service mesh that provides application-level networking to make it easy for your services to communicate with each other across multiple types of compute infrastructure
- standardizes how your services communicate, giving you end-to-end visibility and ensuring high-availability for your applications
- makes it easy to run services by providing consistent visibility and network traffic controls for services built across multiple types of compute infrastructure
- removes the need to update application code to change how monitoring data is collected or traffic is routed between services
- configures each service to export monitoring data and implements consistent communications control logic across your application
- makes it easy to quickly pinpoint the exact location of errors and automatically re-route network traffic when there are failures or when code changes need to be deployed
- uses the open source Envoy proxy
Components
- Service mesh
- logical boundary for network traffic between the services
- Virtual services
- abstratction of a real service that is provided by a virtual node directly or indirectly by means of a virtual router
- Virtual nodes
- acts as a logical pointer to a particular task group
- When you create a virtual node, you must specify the service discovery name for your task group
- Envoy proxy
- configures your microservice task group to use the App Mesh service mesh traffic rules that you set up for your virtual routers and virtual nodes
- add the Envoy container to your task group after you have created your virtual nodes, virtual routers, routes, and virtual services
- Virtual routers
- handles traffic for one or more virtual services within your mesh
- Routes
- associated with a virtual router, and it directs traffic that matches a service name prefix to one or more virtual nodes
- Virtual gateways
- allows resources that are outside of your mesh to communicate to resources that are inside of your mesh
- represents an Envoy proxy running in an Amazon ECS service, in a Kubernetes service, or on an Amazon EC2 instance
- Unlike a virtual node, which represents Envoy running with an application, a virtual gateway represents Envoy deployed by itself
- Gateway routes
- configuration for handling the incoming requests at the Virtual Gateway
- attached to a virtual gateway and routes traffic to an existing virtual service

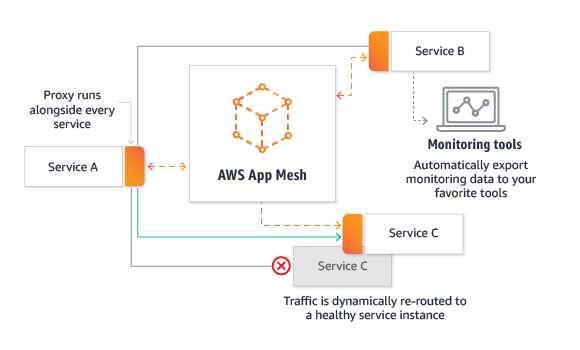
Benefits
- End-to-end visibility
- captures metrics, logs, and traces from all of your applications
- quickly identify and isolate issues with any service to optimize your entire application
- Ensure high availability
- can easily implement custom traffic routing rules to ensure every service is highly available during deployments, after failures, and as your application scales
- Steramline operations
- removes the need to configure communication protocols for each service, write custom code, or implement libraries to operate your application.
- Enhance any application
- can monitor and control communications for monoliths running on EC2, teams running containerized applications, orchestration systems, or VPCs as a single application without any code changes
- End-to-end Encryption
- gives you the ability to encrypt traffic between services using AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) or customer-provided certificates
'AWS > ECS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| VPC Lattice (0) | 2023.09.22 |
|---|---|
| ECS Capacity Providers (0) | 2023.09.17 |
| ECS Networking 정리 (0) | 2023.09.17 |
| ECS Monitoring 정리 (0) | 2023.09.15 |
| ECS 개념 정리 (0) | 2023.09.07 |